Introduction
A queen bee is the most crucial member of a honeybee colony. Her primary function is to lay eggs, and the colony’s survival depends on her egg-laying capacity. Therefore, understanding how many eggs a queen bee lays each day is essential for beekeepers, as it directly affects the colony’s productivity. In this article, we will explore the average number of eggs a queen bee lays each day, the egg-laying process, and the factors that affect it.
The Role of Queen Bees in the Colony
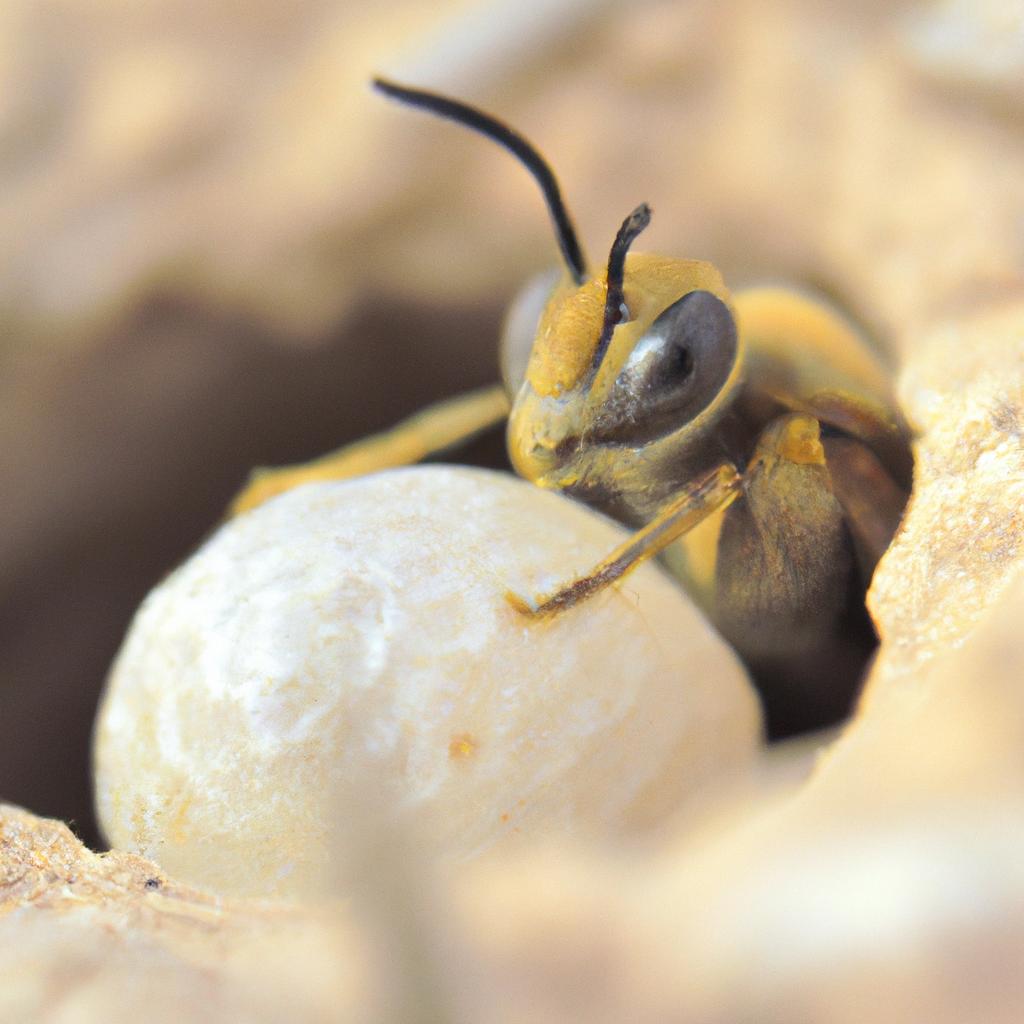

A honeybee colony consists of three types of bees: queen bees, worker bees, and drones. Queen bees are the only sexually mature females in the colony, and their primary function is to lay eggs. They are larger than worker bees and have a distinctive long and slender abdomen. A queen bee can live for up to five years, but their egg-laying capacity decreases with age.
Worker bees are sterile females that perform various tasks such as nursing larvae, collecting nectar and pollen, and defending the hive. They are smaller than queen bees and have a shorter lifespan of around six weeks during the summer months.
Drones are male bees that have a single function: to mate with the queen. They are larger than worker bees and have a stockier build. Drones usually die after mating or are expelled from the hive before winter.
The queen bee’s role in the colony is crucial for its survival. Without a queen bee, the colony cannot produce new bees and will eventually die out. Therefore, a healthy queen bee with a high egg-laying capacity is essential for the colony’s productivity and success.
The Egg-Laying Process of Queen Bees
The egg-laying process of queen bees is fascinating and complex. A queen bee can lay up to 2,000 eggs per day, which is more than her body weight. The egg-laying process begins when the queen bee mates with several drones during her nuptial flight. After mating, the queen stores the sperm in a special organ called the spermatheca, which she uses to fertilize the eggs when she lays them.
When the queen bee is ready to lay an egg, she selects a cell in the comb and curves her abdomen downwards. She then deposits the egg into the cell, which is usually at the bottom of the cell. The queen bee can choose whether to fertilize the egg or not, depending on the needs of the colony. If the egg is fertilized, it will develop into a female bee or worker bee. If the egg is not fertilized, it will develop into a male bee or drone.
The Egg-Laying Process of Queen Bees (Contd.)
The queen bee’s anatomy is different from worker bees and drones, and she has specialized reproductive organs for egg-laying. The queen bee has a longer and more extensive abdomen, which houses the reproductive organs, including the ovaries, spermatheca, and oviducts. The ovaries produce the eggs, the spermatheca stores the sperm, and the oviducts transport the egg from the ovaries to the spermatheca and then to the outside of the queen’s body.
Factors that affect the egg-laying process include the queen bee’s age, genetics, and environmental conditions. As the queen bee ages, her egg-laying capacity decreases, and the eggs’ quality may also decline. Genetics also play a role in the egg-laying process as some queen bees have a higher egg-laying capacity than others. Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and food availability can also affect the egg-laying process.
How Many Eggs Does a Queen Bee Lay Each Day?
On average, a queen bee can lay between 1,500 to 2,000 eggs per day during the peak season, which is usually in the spring and early summer. However, the egg-laying capacity of a queen bee can vary depending on various factors such as genetics, age, and environmental conditions.
The number of eggs laid by a queen bee is also affected by the type of bee. For example, a queen bumblebee can lay up to 400 eggs in her lifetime, while a queen carpenter bee lays around 20 eggs per day. However, these bees have a shorter lifespan than honeybees, and their colonies are smaller.
Factors that affect the number of eggs laid include the availability of food, the size of the colony, and the queen bee’s health. A well-fed queen bee with a large and healthy colony is likely to lay more eggs than a queen bee in a smaller or weaker colony. Beekeepers can also encourage the queen bee to lay more eggs by providing a healthy and stress-free environment, adequate food, and regular colony inspections.
In conclusion, understanding how many eggs a queen bee lays each day is essential for beekeepers to manage their hives effectively. The average number of eggs laid per day varies depending on various factors such as genetics, age, and environmental conditions. Beekeepers can encourage their queen bees to lay more eggs by providing a healthy and stress-free environment, adequate food, and regular colony inspections. By doing so, they can ensure the productivity and success of their honeybee colonies.
Importance of Knowing How Many Eggs a Queen Bee Lays Each Day
Understanding how many eggs a queen bee lays each day is crucial for beekeepers, as it directly impacts the colony’s success. Here are some reasons why:
Impact on the Colony’s Success
The egg-laying capacity of a queen bee determines the number of new bees in the colony. A healthy queen bee lays enough eggs to replace the bees that die and increase the colony’s population. If the queen bee is not laying enough eggs, the colony’s population will decrease, and it may eventually die out. Therefore, monitoring the queen bee’s egg-laying capacity is essential for the colony’s success.
Impact on Honey Production
The number of bees in the colony directly affects honey production. The more bees, the more honey the colony can produce. Therefore, a healthy queen bee with a high egg-laying capacity is essential for honey production. Beekeepers can increase honey production by ensuring that the queen bee is healthy and laying enough eggs.
Importance in Beekeeping Management
Beekeepers must monitor the queen bee’s egg-laying capacity to ensure the colony’s productivity. If the queen bee is not laying enough eggs, beekeepers can replace her with a new queen. They can also stimulate the queen bee’s egg-laying capacity by providing a suitable environment, such as adequate food and water, and maintaining the hive’s temperature and humidity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how many eggs a queen bee lays each day is crucial for beekeeping management and the colony’s success. The queen bee’s egg-laying capacity directly affects the number of bees in the colony, honey production, and overall productivity. Therefore, beekeepers must monitor and manage their hives effectively to ensure the queen bee’s health and egg-laying capacity. By doing so, they can maintain a healthy colony and increase honey production, ultimately benefiting their beekeeping business. Visit BeeKeepinglove.com for more information on beekeeping.
